Zinc is a trace element that’s required for the function of over 300 different enzymes in the human body. It metabolizes nutrients, maintains your immune system, and helps repair body tissues.
Your body doesn’t store Zn, so you need to consume enough every day to ensure that you’re meeting your daily requirements. A lack of Zn can make a person more susceptible to disease and illness.

Currently, the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for Zn in the United States is 8 milligrams (mg) a day for women and 11 mg a day for men. Zn is naturally found in many different foods and is also available as a dietary supplement. The best food sources are high-protein foods like seafood, meat, beans and lentils. Some dairy products also have zinc.
Top Food Sources of Zinc
| Food | Serving Size | Zinc (mg) |
| Oysters | 100 g (3 ½ ounce) | 16.6 |
| Beef | 100 g (3 ½ ounce) | 4.8 |
| Wheat germ | 30 g (1/4 cup) | 5 |
| Pork | 100 g (3 ½ ounce) | 3.2 |
| Heart of palm | 2 hearts | 3 |
| Cheese | 50 g (1 ½ oz) | 1 to 2 |
| Yogurt | 175 mL (3/4 cup) | 1 to 2 |
| Nappa cabbage | 125 mL (1/2 cup) | 2 |
| Turkey | 100 g (3 ½ ounce) | 3.2 |
| Beans | 175 mL (3/4 cup) | 1-2 |
| Lentils | 175 mL (3/4 cup) | 2 |
Zinc and Testosterone
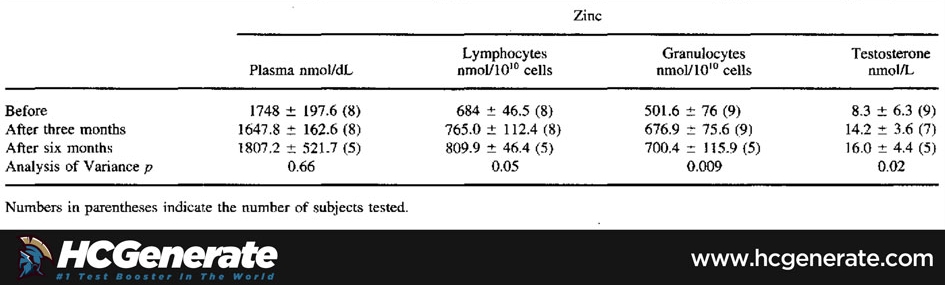
A zinc deficiency can lead to low testosterone. A clinical trial for the Journal of Exercise Physiology found that men who received 30 milligrams of supplemental Zn per day showed increased levels of free testosterone in their bodies [1].
Another study looking at the association of dietary Zn intake and low testosterone levels in healthy men found that Zn supplements increased testosterone levels in Zn deficient men [2].
We conclude that zinc may play an important role in modulating serum testosterone levels in normal men. – Zinc status and serum testosterone levels of healthy adults.
Taking Zn also appears to be helpful if you struggle to recover from high-intensity exercise [3,4].
Other Health Benefits
- Increases Immunity
A clinical trial for the Medical Education Center found that when Zn supplements were administered within 24 hours of the onset of cold-related symptoms, the duration of the symptoms were significantly reduced [5].
- Antioxidant
A clinical trial for the School of Medicine found that levels of oxidative stress markers were significantly lower in the group given Zn supplements. Those with lower Zn levels had higher levels of inflammatory cytokines and higher plasma oxidative stress markers [6].
- Balances Blood Sugar
Zn is needed to balance insulin, the main hormone involved in the regulation of blood sugar. It also allows for the proper utilization of digestive enzymes that are necessary for insulin to bind to cells, so glucose is used as fuel instead of being stored as fat.
- Promotes Heart Health
Zn is needed to maintain the health of cells within the cardiovascular system. It benefits heart health by supporting healthy circulation and is a natural remedy for high blood pressure.
- Aids in Nutrient Absorption and Digestion
Zn is required by the body to use amino acids from foods. It’s also involved in the breakdown of carbohydrates from foods, which are one of the main energy sources for the body.
- Supports Liver Health
Supplementing with zinc is correlated with lower levels of liver damage. It helps with nutrient absorption and allows for proper waste elimination.
- Helps with Muscle Growth and Repair
Zn plays a crucial role in cell division and cell growth. It also helps with the release of testosterone, growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), all of which build muscle mass.
Zinc Supplements
Zinc is not easily absorbed by the body unless it is first attached to another substance. For this reason, many supplement manufacturers chelate it to an amino acid.
Supplemental Zn is also available in the inorganic and non-chelated form called sulfate or oxide. Research studies on the different forms show that the best absorbability comes from using amino acid chelated forms.
N2generate contains 7mg of zinc amino acid chelate in every serving.
References
[1] Meissner, D., Leonhardt, W., Schulze, J., & Julius, U. (1981). Correlations Between Parameters Of Lipoprotein Metabolism And Magnesium, Copper, And Zinc. Hormones, Lipoproteins and Atherosclerosis,91-96. doi:10.1016/b978-0-08-027357-0.50013-5
[2] Prasad, A. (1996). Zinc Status and Serum Testosterone Levels of Healthy Adults. Nutrition,12(5), Vi. doi:10.1016/s0899-9007(96)00064-0
[3] Rabin, R. A., & Jackson, C. G. (1992). Effect Of Aerobic Conditioning On Resting Serum Testosterone Levels In Sedentary Vegetarian And Nonvegetarian Males. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise,24(Supplement). doi:10.1249/00005768-199205001-00301
[4] Jalali, G. R., Roozbeh, J., Mohammadzadeh, A., Sharifian, M., Sagheb, M. M., Jahromi, A. H., . . . Afshariani, R. (2010). Impact of oral zinc therapy on the level of sex hormones in male patients on hemodialysis. Renal Failure,32(4), 417-419. doi:10.3109/08860221003706958
[5] Marshall, I. (1999). Zinc for the common cold. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd001364
[6] Prasad, A. S., Beck, F. W., Bao, B., Fitzgerald, J. T., Snell, D. C., Steinberg, J. D., & Cardozo, L. J. (2007). Zinc supplementation decreases incidence of infections in the elderly: Effect of zinc on generation of cytokines and oxidative stress. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,85(3), 837-844. doi:10.1093/ajcn/85.3.837
Zinc review
-
Lean Muscle Mass Gains
-
Fat Loss
-
Boost Testosterone
-
Enhance Libido