Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin that is most commonly known for its strong antioxidative properties.
The National Institute of Health supports the claim that it may help reduce free radical damage and slow the aging process of your cells [1]. It also has other beneficial effects on your health, such as naturally boosting testosterone levels and improving cardiovascular health.

Vitamin E and Testosterone Levels
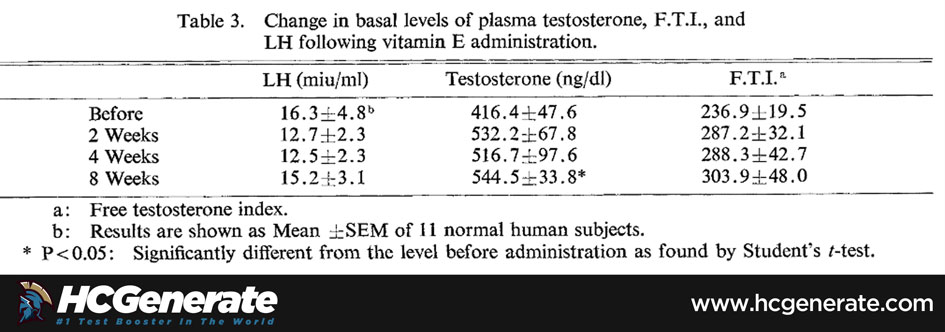
Vitamin E has a strong impact on reproductive health. Animal research clearly indicates that it plays a vital role in the maintenance of male and female fertility [2]. Human clinical trials show that vit E deficiency can cause suppression of testicular activity and decreased production of testosterone. One clinical trial found that men supplementing with 483mg of vit E daily significantly raised levels of total, free, tissue and plasma testosterone [3].
Vit E being a natural anti-estrogen also lowers serum estrogen, suppresses prolactin, and enhances prostate health [4].
Sources of Vitamin E
Vit E naturally occurs in many foods. It’s also available in food fortified with vit E and as a dietary supplement.
Vit E is found in the following foods:
- Nuts, such as almonds, peanuts, and hazelnuts/filberts
- Seeds, such as sunflower seeds
- Green leafy vegetables, such as spinach and broccoli
- Fortified breakfast cereals, fruit juices, margarine, and spreads. Fortified means that vit E has been added to the food.

Achieving Optimal Levels of Vitamin E
I recommend consuming 2-3 of these vit E rich foods daily:
- Sunflower Seeds: 1 cup — 33.41 milligrams
- Almonds: 1 cup — 32.98 milligrams
- Hazelnuts: 1 cup — 20.29 milligrams
- Wheat Germ: 1 cup— 18 milligrams
- Spinach: 1 cup cooked — 3.8 milligrams
- Mango: 1 whole raw — 3.02 milligrams
- Avocado: 1 whole raw — 2.68 milligrams
- Butternut Squash: 1 cup cooked — 2.64 milligrams
- Broccoli: 1 cup cooked — 2.4 milligrams
- Kiwi: 1 medium — 1.1 milligrams
- Tomato: 1 raw — 0.7 milligram
483mg of vit E daily was the dosage used in the clinical trial, where participants saw a significant increase in both free and total testosterone. Rodent studies who received the human equivalent of 1200-1500mg saw even more impressive hormonal gains.
These results suggest that vitamin E may play an important and potent role in hormone production in the pituitary-gonadal axis in humans and rats. – Effect of vitamin E on function of pituitary-gonadal axis in male rats and human subjects.
Achieving those vit E intakes through food alone would be impossible, which is where supplementation comes in. N2generate contains 200mg of highly absorbable vitamin E in each serving.
References
- Traber MG. Vitamin E. In: Shils ME, Shike M, Ross AC, Caballero B, Cousins R, eds. Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease. 10th ed. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006;396-411.
- Aydilek, N., Aksakal, M., & Karakılçık, A. Z. (2004). Effects of testosterone and vitamin E on the antioxidant system in rabbit testis. Andrologia, 36(5), 277-281.
- Sahoo, D. K., Roy, A., & Chainy, G. B. (2008). Protective effects of vitamin E and curcumin on L-thyroxine-induced rat testicular oxidative stress. Chemico-biological interactions, 176(2), 121-128.
- McVey, M. J., Cooke, G. M., Curran, I. H., Chan, H. M., Kubow, S., Lok, E., & Mehta, R. (2008). Effects of dietary fats and proteins on rat testicular steroidogenic enzymes and serum testosterone levels. Food and chemical toxicology, 46(1), 259-269.
Vitamin E review
-
Lean Muscle Mass Gains
-
Fat Loss
-
Boost Testosterone
-
Enhance Libido